
Tamara Bodnar
Job Title
Postdoctoral Fellow
Employer
The University of British Columbia

Review details about the recently announced changes to study and work permits that apply to master’s and doctoral degree students. Read more
The Graduate Program in Neuroscience strives to educate and support graduate students as they expand the breadth and depth of their knowledge about the brain through enriching research experiences. The program embraces principles of equity, diversity and inclusion and recognizes and accommodates individual needs and academic backgrounds. Through two core courses on molecular/cellular and systems neuroscience, respectively, students in the program develop a broadly based and applicable neuroscientific knowledge base. Additional related courses are available for selection by the student and their supervisor. The program is research-oriented and students engage in research from the start of their studies. Research is undertaken in the laboratory of the supervisor and in their affiliated home department, over a wide range of basic and clinical neuroscience topics. With its inter-departmental structure, the program offers collaborative research opportunities that extend beyond the usual boundaries of neuroscience.
The Graduate Program in Neuroscience is a multidisciplinary program administered under the Faculty of Medicine and the Djavad Mowafaghian Centre for Brain Health at the University of British Columbia. It offers a coordinated program of graduate studies leading to MSc and PhD degrees in Neuroscience. The objective of the program is to educate graduate students as neuroscientists with intensive experience in at least one area of research, and to ensure that students in the program develop a broadly based knowledge of the neurosciences.
The program is comprised of more than 120 faculty members representing 20+ departments from the Faculties of Medicine, Science, and Arts at the University of British Columbia. Laboratory and teaching areas are located across the UBC campus, at UBC Hospital and Vancouver General Hospital.
Our faculty have research collaborations that span across departments, industries, and international borders. Although the program is inter-departmental, various regular seminars, journal clubs, and invited lectures provide ample opportunity to meet and discuss current topics in neuroscience. The program encourages its graduate students to participate in the many academic and social events organized by the Djavad Mowafaghian Centre for Brain Health and by the program’s student association.
The Faculty of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies establishes the minimum admission requirements common to all applicants, usually a minimum overall average in the B+ range (76% at UBC). The graduate program that you are applying to may have additional requirements. Please review the specific requirements for applicants with credentials from institutions in:
Each program may set higher academic minimum requirements. Please review the program website carefully to understand the program requirements. Meeting the minimum requirements does not guarantee admission as it is a competitive process.
Applicants from a university outside Canada in which English is not the primary language of instruction must provide results of an English language proficiency examination as part of their application. Tests must have been taken within the last 24 months at the time of submission of your application.
Minimum requirements for the two most common English language proficiency tests to apply to this program are listed below:
Overall score requirement: 100
Reading
22
Writing
21
Speaking
21
Listening
22
Overall score requirement: 7.0
Reading
6.5
Writing
6.5
Speaking
6.5
Listening
6.5
Some programs require additional test scores such as the Graduate Record Examination (GRE) or the Graduate Management Test (GMAT). The requirements for this program are:
The GRE is not required.
Deadline to submit online application. No changes can be made to the application after submission.
Transcript DeadlineDeadline to upload scans of official transcripts through the applicant portal in support of a submitted application. Information for accessing the applicant portal will be provided after submitting an online application for admission.
Referee DeadlineDeadline for the referees identified in the application for admission to submit references. See Letters of Reference for more information.
All applicants have to submit transcripts from all past post-secondary study. Document submission requirements depend on whether your institution of study is within Canada or outside of Canada.
A minimum of three references are required for application to graduate programs at UBC. References should be requested from individuals who are prepared to provide a report on your academic ability and qualifications.
Many programs require a statement of interest, sometimes called a "statement of intent", "description of research interests" or something similar.
Students in research-based programs usually require a faculty member to function as their thesis supervisor. Please follow the instructions provided by each program whether applicants should contact faculty members.
Whereas a commitment from a supervisor is not required prior to applying to the program, a supervisor is required for admission. Please view Graduate Program in Neuroscience faculty here: https://neuroscience.ubc.ca/faculty/. When contacting potential supervisors, we recommend including a CV, unofficial academic transcript, and a brief and specific explanation of why you are interested in joining that particular lab.
Permanent Residents of Canada must provide a clear photocopy of both sides of the Permanent Resident card.
All applicants must complete an online application form and pay the application fee to be considered for admission to UBC.
With more than 155,000 square feet of space, the Djavad Mowafaghian Centre for Brain Health has both laboratory and clinical research areas within the Centre proper and in the UBC Hospital Koerner Pavilion. Our core facilities are essential to ongoing collaboration, teaching, and research.
| Fees | Canadian Citizen / Permanent Resident / Refugee / Diplomat | International |
|---|---|---|
| Application Fee | $116.25 | $168.25 |
| Tuition * | ||
| Installments per year | 3 | 3 |
| Tuition per installment | $1,875.34 | $3,294.66 |
| Tuition per year (plus annual increase, usually 2%-5%) | $5,626.02 | $9,883.98 |
| Int. Tuition Award (ITA) per year (if eligible) | $3,200.00 (-) | |
| Other Fees and Costs | ||
| Student Fees (yearly) | $1,144.10 (approx.) | |
| Costs of living | Estimate your costs of living with our interactive tool in order to start developing a financial plan for your graduate studies. | |
Applicants to UBC have access to a variety of funding options, including merit-based (i.e. based on your academic performance) and need-based (i.e. based on your financial situation) opportunities.
There is a minimum funding stipend provided by each supervisor. For more information, please visit Minimum Funding for Students. For both MSc and PhD students, the Department follows a minimum funding support guideline. For PhD students, starting September 2025, the stipend will be $35,000 in year 1, $37,500 in year 2, and $40,000 annually in years 3 and 4. For MSc students, the stipend is $26,000 for year 1 and $30,000 for year 2. This stipend can come in any form (for example – scholarship, TA-ship, grant funding, or a combination).
This results in a net balance (any funding provided to the student minus tuition and fees) mean of $35,269 and median of $35,255.
All applicants are encouraged to review the awards listing to identify potential opportunities to fund their graduate education. The database lists merit-based scholarships and awards and allows for filtering by various criteria, such as domestic vs. international or degree level.
Many professors are able to provide Research Assistantships (GRA) from their research grants to support full-time graduate students studying under their supervision. The duties constitute part of the student's graduate degree requirements. A Graduate Research Assistantship is considered a form of fellowship for a period of graduate study and is therefore not covered by a collective agreement. Stipends vary widely, and are dependent on the field of study and the type of research grant from which the assistantship is being funded.
Graduate programs may have Teaching Assistantships available for registered full-time graduate students. Full teaching assistantships involve 12 hours work per week in preparation, lecturing, or laboratory instruction although many graduate programs offer partial TA appointments at less than 12 hours per week. Teaching assistantship rates are set by collective bargaining between the University and the Teaching Assistants' Union.
Academic Assistantships are employment opportunities to perform work that is relevant to the university or to an individual faculty member, but not to support the student’s graduate research and thesis. Wages are considered regular earnings and when paid monthly, include vacation pay.
Canadian and US applicants may qualify for governmental loans to finance their studies. Please review eligibility and types of loans.
All students may be able to access private sector or bank loans.
Many foreign governments provide support to their citizens in pursuing education abroad. International applicants should check the various governmental resources in their home country, such as the Department of Education, for available scholarships.
The possibility to pursue work to supplement income may depend on the demands the program has on students. It should be carefully weighed if work leads to prolonged program durations or whether work placements can be meaningfully embedded into a program.
International students enrolled as full-time students with a valid study permit can work on campus for unlimited hours and work off-campus for no more than 24 hours a week during academic sessions.
A good starting point to explore student jobs is the UBC Work Learn program or a Co-Op placement.
Students with taxable income in Canada may be able to claim federal or provincial tax credits.
Canadian residents with RRSP accounts may be able to use the Lifelong Learning Plan (LLP) which allows students to withdraw amounts from their registered retirement savings plan (RRSPs) to finance full-time training or education for themselves or their partner.
Please review Filing taxes in Canada on the student services website for more information.
Applicants have access to the cost estimator to develop a financial plan that takes into account various income sources and expenses.
92 students graduated between 2005 and 2013: 2 are in non-salaried situations; for 6 we have no data (based on research conducted between Feb-May 2016). For the remaining 84 graduates:
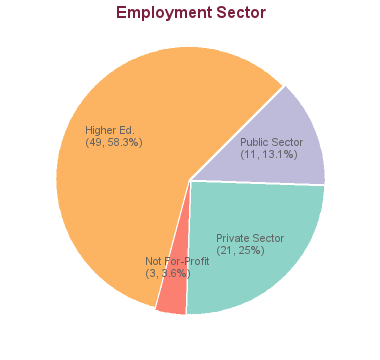
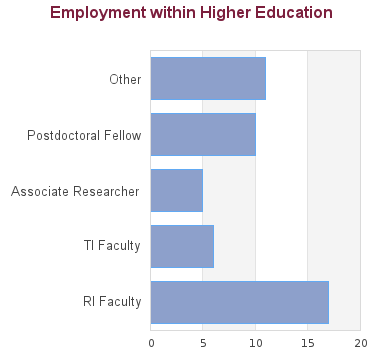
The 6-7 year PhD in Neuroscience is designed to prepare students for employment in the public or private sector, or to pursue further studies in the PhD program. Recent graduates have taken positions at Johnson & Johnson, AstraZeneca, Weston Brain Institute, BC Cancer Center, Science World and many other organizations. Those looking to pursue a postdoc in Neuroscience have gone on to study at other universities such as McGill as well as our own PhD program.
These statistics show data for the Doctor of Philosophy in Neuroscience (PhD). Data are separated for each degree program combination. You may view data for other degree options in the respective program profile.
| 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Applications | 58 | 58 | 53 | 43 | 40 |
| Offers | 11 | 12 | 12 | 13 | 9 |
| New Enrolment | 9 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 6 |
| Total Enrolment | 81 | 88 | 76 | 68 | 64 |
Students in research-based programs usually require a faculty member to function as their thesis supervisor. Please follow the instructions provided by each program whether applicants should contact faculty members.
Whereas a commitment from a supervisor is not required prior to applying to the program, a supervisor is required for admission. Please view Graduate Program in Neuroscience faculty here: https://neuroscience.ubc.ca/faculty/. When contacting potential supervisors, we recommend including a CV, unofficial academic transcript, and a brief and specific explanation of why you are interested in joining that particular lab.
These videos contain some general advice from faculty across UBC on finding and reaching out to a supervisor. They are not program specific.
| Year | Citation |
|---|---|
| 2010 | Dr. Barakauskas measured several presynaptic proteins in brain samples, developing and validating new methods to do so. Some of these proteins were altered in distinct regions of the striatum in post-mortem brain samples of subjects with schizophrenia. These findings implicate these proteins in brain dysfunction in patients. |
| 2010 | Dr. Zhou studied the cellular mechanisms underlying spreading depression, the propagating depolarization that underlies the aura of migraine. She discovered that a novel form of regenerative glutamate-release generates spreading depression independent of classical synaptic transmission. This research provides insight into migraine pathophysiology and potential new therapeutic targets. |
| 2010 | Dr. Palmer used functional imaging methods to study the compensatory mechanisms used by the brain in Parkinson's Disease. She identified a compensatory switch to alternative motor networks including the cerebellum. Understanding these mechanisms is important for development of new drug targets and better therapies. |
| 2010 | Dr. Barker showed that new neurons in the adult rat brain respond to the presence of estradiol in females but not in males. This research highlights the importance of studying both sexes when developing basic descriptions of biological phenomena and potential therapies for neurodegenerative diseases. |
| 2010 | Dr. Ge studied the role of synaptic plasticity in spatial memory, and how synaptic plasticity is modulated by AMPA receptor trafficking. Her work provides a better understanding of how different forms of synaptic plasticity contribute to the process of spatial memory formation. |
| 2010 | Dr. Vasuta examined how the function of a major receptor in the brain is regulated. This receptor mediates excitation in the nervous system, and is linked to learning and memory formation. She proved that exercise influences synaptic phenomena that may be the basis of memory acquisition and consolidation. |
| 2010 | Dr. Wong identified the first natural marine compound that can enhance axon outgrowth in the adult central nervous system. Using motile cells to model the neuronal growth cone, the basic machinery underlying axon outgrowth, she designed a high-throughput screen to identify the first cyclic dipeptide that promoted axon regeneration in vitro, as well as axon sprouting and behavioural improvements in vivo. |
| 2009 | Dr. Hewapathirane created a novel experimental model to study the effects of seizures on brain development. Using this system, he found that early-life seizures inhibit the structural maturation of neuronal cells within the brain. His findings uncovered a potential mechanism through which childhood seizures may induce neurological deficits. |
| 2009 | Dr. Tai studied the cholinergic modulation of three Ca2+-permable ion channels (R-type VGCCs, TRPC5 channels and NMDA receptors) in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons and the potential functional roles of these modulations in both physiological and pathophysiological conditions. His finding helps to develop treatments for epilepsy and ischemia. |
| 2009 | Dr. Lett used a mouse model system to demonstrate how a previously unknown guidance cue is critical for the proper formation of specific tracts during neurodevelopment. This research provides novel insight toward a better understanding of neural network formation and neurological dysfunction resulting from erroneous neurodevelopment. |
Neuroscience offers these core courses: Neuroanatomy, Neurophysiology, Neurochemistry, Psychobiology, Molecular Neurobiology, and Neuropharmacology.
Departments/Programs may update graduate degree program details through the Faculty & Staff portal. To update contact details for application inquiries, please use this form.

The metropolitan area is known for its diversity and UBC is one of the most international universities in Canada. This multicultural community means we have a wide range of restaurants, grocery stores, and events to provide a sense of belonging.