Veronica Letawsky
Doctor of Philosophy in Audiology and Speech Sciences (PhD)
Exploring salivary changes and effects on swallow physiology and perception in chronic autoimmune disease.
Review details about the recently announced changes to study and work permits that apply to master’s and doctoral degree students. Read more
For the past 50 years, the School of Audiology and Speech Sciences has endeavoured to advance knowledge of human communication, its disorders, and related areas by actively engaging in research, and by educating individuals to become audiologists, speech-language pathologists, and researchers. In its teaching and research programs, the School emphasizes both the importance of basic science to the understanding of communication disorders and the relevance of clinical data to theories of human communication.
The School offers a program leading to the Ph.D. with professional specialty in one of the following areas: acquired language and cognitive communication disorders, bilingualism, developmental language disorders, developmental phonetics and phonology, discourse analysis, dysphagia, electrophysiologic and otoacoustic emissions diagnosis, hearing science, language acquisition, phonological and phonetic disorders, psycholinguistics, speech perception, and speech understanding in the elderly.
The School of Audiology and Speech Sciences (SASS) in the Faculty of Medicine at UBC is the only Ph.D. program in British Columbia that offers doctoral education in the field of human communication, its disorders, and related areas.
SASS faculty are internationally renowned for their research. In addition to mentoring and training Ph.D. students, faculty members are regularly sought after to provide specific expertise. They often introduce cutting-edge techniques used by clinicians and institutions throughout B.C., across Canada, and around the world.
The School can provide the unique opportunity of completing coursework and clinical training required for certification as an audiologist or speech-language pathologist within the doctoral program of studies. Currently, any prospective student considering this option must first apply to enter the Master of Science in either audiology or speech-language pathology. Applicants must meet all of the MSc admission requirements. Although the MSc application is not a formal application to the PhD program, prospective students interested in continuing into the PhD program should indicate this in their Statement of Interest.
Eligibility for admission will be decided by the Doctoral Studies Committee. The Committee will consist of the Graduate Advisor and a minimum of three other full members of the graduate faculty who are full-time faculty at the School.
The Faculty of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies establishes the minimum admission requirements common to all applicants, usually a minimum overall average in the B+ range (76% at UBC). The graduate program that you are applying to may have additional requirements. Please review the specific requirements for applicants with credentials from institutions in:
Each program may set higher academic minimum requirements. Please review the program website carefully to understand the program requirements. Meeting the minimum requirements does not guarantee admission as it is a competitive process.
Applicants from a university outside Canada in which English is not the primary language of instruction must provide results of an English language proficiency examination as part of their application. Tests must have been taken within the last 24 months at the time of submission of your application.
Minimum requirements for the two most common English language proficiency tests to apply to this program are listed below:
Overall score requirement: 100
Reading
22
Writing
21
Speaking
21
Listening
22
Overall score requirement: 7.0
Reading
6.0
Writing
6.0
Speaking
6.0
Listening
6.0
Some programs require additional test scores such as the Graduate Record Examination (GRE) or the Graduate Management Test (GMAT). The requirements for this program are:
The GRE is not required.
An applicant to the doctoral program should have completed a master's degree, typically in audiology and speech sciences, psychology, linguistics, or a related discipline.
If you are a non-native English speaker, and you do not have at least four years of continuous post-secondary education in an English-speaking university, you must provide proof of proficiency in English by meeting the following two requirements: 1. Upload a copy of your official test scores from either the TOEFL or IELTS tests, ensuring that you meet the minimum stated individual component scores AND the overall score for admission to our program. Tests must have been taken within the last 24 months at the time of submission of your application. Minimum scores must be achieved in a single sitting of the test (i.e., scores across multiple instances of a test may not be used to satisfy minimum component requirements). 2. Provide the School with a five to ten-minute recording of your speech. This speech sample may be on any topic, as long as it is neither read nor recited. An interview may follow. You should submit your recording to the School by e-mail to inquiry@audiospeech.ubc.ca as an attached electronic audio file (e.g., MP3).
Please indicate in your application if you would like to be considered for full-time or part-time classification for your PhD. Note: we are unable to change a student status (from part-time study to full-time study and vice versa) once the program has started. A maximum 8-year time period is allowed for completion of the part-time doctoral program (compared to a 6-year time period for full-time students).
All applicants have to submit transcripts from all past post-secondary study. Document submission requirements depend on whether your institution of study is within Canada or outside of Canada.
Many programs require a statement of interest, sometimes called a "statement of intent", "description of research interests" or something similar.
Students in research-based programs usually require a faculty member to function as their thesis supervisor. Please follow the instructions provided by each program whether applicants should contact faculty members.
Permanent Residents of Canada must provide a clear photocopy of both sides of the Permanent Resident card.
All applicants must complete an online application form and pay the application fee to be considered for admission to UBC.
Students are required to take courses in research methodology and in major and minor areas of specialization, with the sequence of courses and seminars totaling at least 18 credits beyond the master's degree. All doctoral students are required to successfully complete a comprehensive examination. The major requirement for the Ph.D. is completion of a research dissertation meeting the Faculty of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies requirements.
| Fees | Canadian Citizen / Permanent Resident / Refugee / Diplomat | International |
|---|---|---|
| Application Fee | $118.50 | $168.25 |
| Tuition * | ||
| Installments per year | 3 | 3 |
| Tuition per installment | $1,875.34 | $3,294.66 |
| Tuition per year (plus annual increase, usually 2%-5%) | $5,626.02 | $9,883.98 |
| Int. Tuition Award (ITA) per year (if eligible) | $3,200.00 (-) | |
| Other Fees and Costs | ||
| Student Fees (yearly) | $1,144.10 (approx.) | |
| Costs of living | Estimate your costs of living with our interactive tool in order to start developing a financial plan for your graduate studies. | |
Applicants to UBC have access to a variety of funding options, including merit-based (i.e. based on your academic performance) and need-based (i.e. based on your financial situation) opportunities.
From September 2024 all full-time students in UBC-Vancouver PhD programs will be provided with a funding package of at least $24,000 for each of the first four years of their PhD. The funding package may consist of any combination of internal or external awards, teaching-related work, research assistantships, and graduate academic assistantships. Please note that many graduate programs provide funding packages that are substantially greater than $24,000 per year. Please check with your prospective graduate program for specific details of the funding provided to its PhD students.
This results in a net balance (any funding provided to the student minus tuition and fees) mean of $4,702 and median of $1,745.
All applicants are encouraged to review the awards listing to identify potential opportunities to fund their graduate education. The database lists merit-based scholarships and awards and allows for filtering by various criteria, such as domestic vs. international or degree level.
Many professors are able to provide Research Assistantships (GRA) from their research grants to support full-time graduate students studying under their supervision. The duties constitute part of the student's graduate degree requirements. A Graduate Research Assistantship is considered a form of fellowship for a period of graduate study and is therefore not covered by a collective agreement. Stipends vary widely, and are dependent on the field of study and the type of research grant from which the assistantship is being funded.
Graduate programs may have Teaching Assistantships available for registered full-time graduate students. Full teaching assistantships involve 12 hours work per week in preparation, lecturing, or laboratory instruction although many graduate programs offer partial TA appointments at less than 12 hours per week. Teaching assistantship rates are set by collective bargaining between the University and the Teaching Assistants' Union.
Academic Assistantships are employment opportunities to perform work that is relevant to the university or to an individual faculty member, but not to support the student’s graduate research and thesis. Wages are considered regular earnings and when paid monthly, include vacation pay.
Canadian and US applicants may qualify for governmental loans to finance their studies. Please review eligibility and types of loans.
All students may be able to access private sector or bank loans.
UBC has working agreements with MPower Financing - an organization providing international students with no-cosigner, no-collateral education loans to study in Canada - and Windmill Microlending - an organization providing loans to skilled immigrants.
Many foreign governments provide support to their citizens in pursuing education abroad. International applicants should check the various governmental resources in their home country, such as the Department of Education, for available scholarships.
The possibility to pursue work to supplement income may depend on the demands the program has on students. It should be carefully weighed if work leads to prolonged program durations or whether work placements can be meaningfully embedded into a program.
International students enrolled as full-time students with a valid study permit can work on campus for unlimited hours and work off-campus for no more than 24 hours a week during academic sessions.
A good starting point to explore student jobs is the UBC Work Learn program or a Co-Op placement.
Students with taxable income in Canada may be able to claim federal or provincial tax credits.
Canadian residents with RRSP accounts may be able to use the Lifelong Learning Plan (LLP) which allows students to withdraw amounts from their registered retirement savings plan (RRSPs) to finance full-time training or education for themselves or their partner.
Please review Filing taxes in Canada on the student services website for more information.
Applicants have access to the cost estimator to develop a financial plan that takes into account various income sources and expenses.
7 students graduated between 2005 and 2013. Of these, career information was obtained for 7 alumni (based on research conducted between Feb-May 2016):
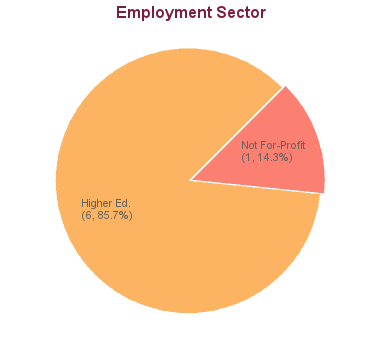
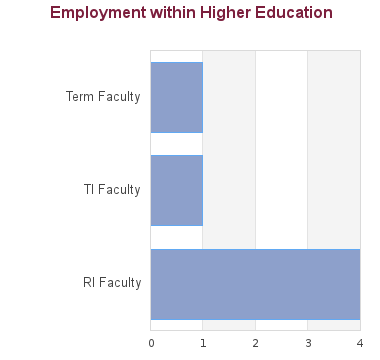
There is a shortage of academic personnel throughout North America. A PhD in Audiology or Speech-Language Pathology can open many doors, both inside and outside of academia. The School’s Ph.D. graduates have been successful at obtaining positions at academic institutions, as well as leadership positions in the professional community. PhD training provides the skills to carry out one’s own research, as well as to participate in research teams. Faculty positions at universities allow one to teach tomorrow’s rising stars, while conducting research that informs knowledge and practice. University faculty positions are highly flexible, often provide sabbatical leaves, and can provide the security of tenure. Salaries for faculty show substantial growth, with far less of a “ceiling” than other jobs. Positions for those with doctorates are also widely available outside of universities. The skills attained with a PhD are required for many high-level jobs in universities, hospitals, clinics, private industries, and public organizations.
These statistics show data for the Doctor of Philosophy in Audiology and Speech Sciences (PhD). Data are separated for each degree program combination. You may view data for other degree options in the respective program profile.
| 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Applications | 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 |
| Offers | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 3 |
| New Enrolment | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 3 |
| Total Enrolment | 7 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 7 |
Students in research-based programs usually require a faculty member to function as their thesis supervisor. Please follow the instructions provided by each program whether applicants should contact faculty members.
These videos contain some general advice from faculty across UBC on finding and reaching out to a supervisor. They are not program specific.
This list shows faculty members with full supervisory privileges who are affiliated with this program. It is not a comprehensive list of all potential supervisors as faculty from other programs or faculty members without full supervisory privileges can request approvals to supervise graduate students in this program.
Audiology and Speech Sciences endeavours to advance knowledge of human communication and its disorders by actively engaging in research, and by educating individuals to become audiologists, speech-language pathologists, and researchers.
Departments/Programs may update graduate degree program details through the Faculty & Staff portal. To update contact details for application inquiries, please use this form.
