Meghna Mohandas
Doctor of Philosophy in Planning (PhD)
Private space as sites of ‘othering’: Housing experiences of Indigenous migrant women in Bengaluru, India
Review details about the recently announced changes to study and work permits that apply to master’s and doctoral degree students. Read more
SCARP’s mission is to, through education and research, generate and transform knowledge into action by planning in partnership to improve lives and communities and the quality of built and natural environments. We are interested in attracting students to our PhD program who are interested in gaining the capabilities of a planning scholar – including deep awareness of intellectual history and planning theory, the diverse research designs employed in planning research, and in specific research methodologies – data collection and analysis. Planning scholarship touches on issues of participatory democracy, policy, and social and environmental change in place-based communities. Explicit connection of knowledge to action distinguishes planning research from that of many other disciplines.
SCARP’s faculty have diverse areas of expertise and interest that prospective students are encouraged to seek out, including sustainable/active transportation, disaster and resilience planning, social planning, place-based health and care planning, climate adaptation and energy transition, cross-cultural and indigenous planning, housing and infrastructure planning, community based urban design, and urbanisation and its challenges in the Global South, to name just a few of our faculty's research interests. Our research approach is inherently interdisciplinary and spans qualitative, quantitative, and participatory/action methodologies.
The Faculty of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies establishes the minimum admission requirements common to all applicants, usually a minimum overall average in the B+ range (76% at UBC). The graduate program that you are applying to may have additional requirements. Please review the specific requirements for applicants with credentials from institutions in:
Each program may set higher academic minimum requirements. Please review the program website carefully to understand the program requirements. Meeting the minimum requirements does not guarantee admission as it is a competitive process.
Applicants from a university outside Canada in which English is not the primary language of instruction must provide results of an English language proficiency examination as part of their application. Tests must have been taken within the last 24 months at the time of submission of your application.
Minimum requirements for the two most common English language proficiency tests to apply to this program are listed below:
Overall score requirement: 100
Reading
22
Writing
21
Speaking
21
Listening
22
Overall score requirement: 7.0
Reading
6.5
Writing
6.5
Speaking
6.5
Listening
6.5
Some programs require additional test scores such as the Graduate Record Examination (GRE) or the Graduate Management Test (GMAT). The requirements for this program are:
The GRE is optional.
All applicants have to submit transcripts from all past post-secondary study. Document submission requirements depend on whether your institution of study is within Canada or outside of Canada.
Many programs require a statement of interest, sometimes called a "statement of intent", "description of research interests" or something similar.
Students in research-based programs usually require a faculty member to function as their thesis supervisor. Please follow the instructions provided by each program whether applicants should contact faculty members.
Permanent Residents of Canada must provide a clear photocopy of both sides of the Permanent Resident card.
All applicants must complete an online application form and pay the application fee to be considered for admission to UBC.
| Fees | Canadian Citizen / Permanent Resident / Refugee / Diplomat | International |
|---|---|---|
| Application Fee | $118.50 | $168.25 |
| Tuition * | ||
| Installments per year | 3 | 3 |
| Tuition per installment | $1,875.34 | $3,294.66 |
| Tuition per year (plus annual increase, usually 2%-5%) | $5,626.02 | $9,883.98 |
| Int. Tuition Award (ITA) per year (if eligible) | $3,200.00 (-) | |
| Other Fees and Costs | ||
| Student Fees (yearly) | $1,144.10 (approx.) | |
| Costs of living | Estimate your costs of living with our interactive tool in order to start developing a financial plan for your graduate studies. | |
Applicants to UBC have access to a variety of funding options, including merit-based (i.e. based on your academic performance) and need-based (i.e. based on your financial situation) opportunities.
As of September 2025, all full-time students in UBC-Vancouver PhD programs will be provided with a funding package of at least $40,000 for each of the first four years of their PhD. The funding package may consist of any combination of internal or external awards, teaching-related work, research assistantships, and graduate academic assistantships. Funding packages are developed specifically for each admitted student, dependent on their area of research, experience, and supervisor’s project. Please note that the $40,000/year package developed is a minimum and students often receive annual funding greater than this amount through their participation in funded research projects, awards and scholarships, and teaching assistantships.
This results in a net balance (any funding provided to the student minus tuition and fees) mean of $54,255 and median of $61,532.
All applicants are encouraged to review the awards listing to identify potential opportunities to fund their graduate education. The database lists merit-based scholarships and awards and allows for filtering by various criteria, such as domestic vs. international or degree level.
Many professors are able to provide Research Assistantships (GRA) from their research grants to support full-time graduate students studying under their supervision. The duties constitute part of the student's graduate degree requirements. A Graduate Research Assistantship is considered a form of fellowship for a period of graduate study and is therefore not covered by a collective agreement. Stipends vary widely, and are dependent on the field of study and the type of research grant from which the assistantship is being funded.
Graduate programs may have Teaching Assistantships available for registered full-time graduate students. Full teaching assistantships involve 12 hours work per week in preparation, lecturing, or laboratory instruction although many graduate programs offer partial TA appointments at less than 12 hours per week. Teaching assistantship rates are set by collective bargaining between the University and the Teaching Assistants' Union.
Academic Assistantships are employment opportunities to perform work that is relevant to the university or to an individual faculty member, but not to support the student’s graduate research and thesis. Wages are considered regular earnings and when paid monthly, include vacation pay.
Canadian and US applicants may qualify for governmental loans to finance their studies. Please review eligibility and types of loans.
All students may be able to access private sector or bank loans.
UBC has working agreements with MPower Financing - an organization providing international students with no-cosigner, no-collateral education loans to study in Canada - and Windmill Microlending - an organization providing loans to skilled immigrants.
Many foreign governments provide support to their citizens in pursuing education abroad. International applicants should check the various governmental resources in their home country, such as the Department of Education, for available scholarships.
The possibility to pursue work to supplement income may depend on the demands the program has on students. It should be carefully weighed if work leads to prolonged program durations or whether work placements can be meaningfully embedded into a program.
International students enrolled as full-time students with a valid study permit can work on campus for unlimited hours and work off-campus for no more than 24 hours a week during academic sessions.
A good starting point to explore student jobs is the UBC Work Learn program or a Co-Op placement.
Students with taxable income in Canada may be able to claim federal or provincial tax credits.
Canadian residents with RRSP accounts may be able to use the Lifelong Learning Plan (LLP) which allows students to withdraw amounts from their registered retirement savings plan (RRSPs) to finance full-time training or education for themselves or their partner.
Please review Filing taxes in Canada on the student services website for more information.
Applicants have access to the cost estimator to develop a financial plan that takes into account various income sources and expenses.
22 students graduated between 2005 and 2013. Of these, career information was obtained for 22 alumni (based on research conducted between Feb-May 2016):
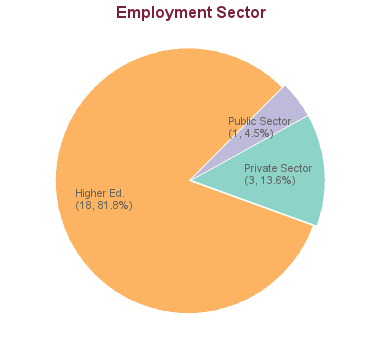
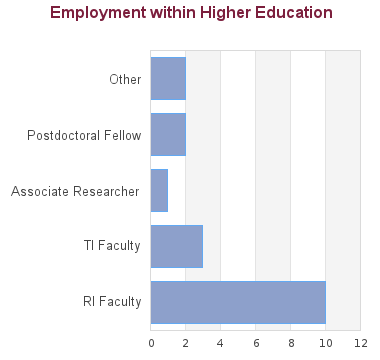
These statistics show data for the Doctor of Philosophy in Planning (PhD). Data are separated for each degree program combination. You may view data for other degree options in the respective program profile.
| 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Enrolment | 2 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 3 |
| Total Enrolment | 19 | 22 | 23 | 22 | 23 |
Students in research-based programs usually require a faculty member to function as their thesis supervisor. Please follow the instructions provided by each program whether applicants should contact faculty members.
This list shows faculty members with full supervisory privileges who are affiliated with this program. It is not a comprehensive list of all potential supervisors as faculty from other programs or faculty members without full supervisory privileges can request approvals to supervise graduate students in this program.
Planning emphasizes an integrated approach that encompasses urban policy and community development, international development, environmental and natural resources, urban design, and planning processes and methods.
Departments/Programs may update graduate degree program details through the Faculty & Staff portal. To update contact details for application inquiries, please use this form.
