
Michael Hoff
Job Title
Assistant Professor
Employer
University of Washington
Applicants to Master’s and Doctoral degrees are not affected by the recently announced cap on study permits. Review more details
The Department of Physics and Astronomy is a broad-based department with a wide range of research interests covering many key topics in contemporary physics, astronomy, and applied physics. We are a vibrant community that engages in a wide range of research directions, from probing the origin of the universe to exploring emergent phenomena in complex systems, that provide deep insights into the nature of the universe and practical solutions that will help define the world of tomorrow. Departmental research activities are supported by several computing and experimental facilities, and excellent electronics and machine shops.
Our graduate programs include approximately 200 graduate students, working on experiments and theory in research fields that include: Applied Physics, Astronomy/Astrophysics, Atomic/Molecular/Optics, Biophysics, Condensed Matter, Cosmology, Gravity, Medical Physics, Nuclear Physics, Particle Physics, and String Theory.
The Department of Physics & Astronomy at UBC is noted for the excellence of its research and its high academic standards and integrity. It is one of the largest and most diverse physics and astronomy departments in Canada. We are constantly rated as one of the top Physics & Astronomy programs in the world. Much of the Department's research is enhanced by local facilities such as the TRIUMF National Laboratory, the Advanced Materials and Process Engineering Laboratory (AMPEL), and the BC Cancer Agency, UBC, and associated teaching hospitals, in addition to many specialized research laboratories housed within the Department. There is a great deal of collaboration and overlap of interests among the various groups.
Each year, our faculty bring over $20 million in research grants. This enables us to maintain world-class research laboratories and computational facilities, attract distinguished post-doctorate researchers, and support highly skilled engineers and technicians whose expertise is critical to our research.
The Faculty of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies establishes the minimum admission requirements common to all applicants, usually a minimum overall average in the B+ range (76% at UBC). The graduate program that you are applying to may have additional requirements. Please review the specific requirements for applicants with credentials from institutions in:
Each program may set higher academic minimum requirements. Please review the program website carefully to understand the program requirements. Meeting the minimum requirements does not guarantee admission as it is a competitive process.
Applicants from a university outside Canada in which English is not the primary language of instruction must provide results of an English language proficiency examination as part of their application. Tests must have been taken within the last 24 months at the time of submission of your application.
Minimum requirements for the two most common English language proficiency tests to apply to this program are listed below:
Overall score requirement: 90
Reading
22
Writing
21
Speaking
21
Listening
22
Overall score requirement: 6.5
Reading
6.0
Writing
6.0
Speaking
6.0
Listening
6.0
Some programs require additional test scores such as the Graduate Record Examination (GRE) or the Graduate Management Test (GMAT). The requirements for this program are:
The GRE is not required.
All applicants have to submit transcripts from all past post-secondary study. Document submission requirements depend on whether your institution of study is within Canada or outside of Canada.
A minimum of three references are required for application to graduate programs at UBC. References should be requested from individuals who are prepared to provide a report on your academic ability and qualifications.
Many programs require a statement of interest, sometimes called a "statement of intent", "description of research interests" or something similar.
Students in research-based programs usually require a faculty member to function as their thesis supervisor. Please follow the instructions provided by each program whether applicants should contact faculty members.
Permanent Residents of Canada must provide a clear photocopy of both sides of the Permanent Resident card.
All applicants must complete an online application form and pay the application fee to be considered for admission to UBC.
| Fees | Canadian Citizen / Permanent Resident / Refugee / Diplomat | International |
|---|---|---|
| Application Fee | $114.00 | $168.25 |
| Tuition * | ||
| Installments per year | 3 | 3 |
| Tuition per installment | $1,838.57 | $3,230.06 |
| Tuition per year (plus annual increase, usually 2%-5%) | $5,515.71 | $9,690.18 |
| Int. Tuition Award (ITA) per year (if eligible) | $3,200.00 (-) | |
| Other Fees and Costs | ||
| Student Fees (yearly) | $1,116.60 (approx.) | |
| Costs of living | Estimate your costs of living with our interactive tool in order to start developing a financial plan for your graduate studies. | |
Applicants to UBC have access to a variety of funding options, including merit-based (i.e. based on your academic performance) and need-based (i.e. based on your financial situation) opportunities.
From September 2024 all full-time students in UBC-Vancouver PhD programs will be provided with a funding package of at least $24,000 for each of the first four years of their PhD. The funding package may consist of any combination of internal or external awards, teaching-related work, research assistantships, and graduate academic assistantships. Please note that many graduate programs provide funding packages that are substantially greater than $24,000 per year. Please check with your prospective graduate program for specific details of the funding provided to its PhD students.
All applicants are encouraged to review the awards listing to identify potential opportunities to fund their graduate education. The database lists merit-based scholarships and awards and allows for filtering by various criteria, such as domestic vs. international or degree level.
Many professors are able to provide Research Assistantships (GRA) from their research grants to support full-time graduate students studying under their supervision. The duties constitute part of the student's graduate degree requirements. A Graduate Research Assistantship is considered a form of fellowship for a period of graduate study and is therefore not covered by a collective agreement. Stipends vary widely, and are dependent on the field of study and the type of research grant from which the assistantship is being funded.
Graduate programs may have Teaching Assistantships available for registered full-time graduate students. Full teaching assistantships involve 12 hours work per week in preparation, lecturing, or laboratory instruction although many graduate programs offer partial TA appointments at less than 12 hours per week. Teaching assistantship rates are set by collective bargaining between the University and the Teaching Assistants' Union.
Academic Assistantships are employment opportunities to perform work that is relevant to the university or to an individual faculty member, but not to support the student’s graduate research and thesis. Wages are considered regular earnings and when paid monthly, include vacation pay.
Canadian and US applicants may qualify for governmental loans to finance their studies. Please review eligibility and types of loans.
All students may be able to access private sector or bank loans.
Many foreign governments provide support to their citizens in pursuing education abroad. International applicants should check the various governmental resources in their home country, such as the Department of Education, for available scholarships.
The possibility to pursue work to supplement income may depend on the demands the program has on students. It should be carefully weighed if work leads to prolonged program durations or whether work placements can be meaningfully embedded into a program.
International students enrolled as full-time students with a valid study permit can work on campus for unlimited hours and work off-campus for no more than 20 hours a week.
A good starting point to explore student jobs is the UBC Work Learn program or a Co-Op placement.
Students with taxable income in Canada may be able to claim federal or provincial tax credits.
Canadian residents with RRSP accounts may be able to use the Lifelong Learning Plan (LLP) which allows students to withdraw amounts from their registered retirement savings plan (RRSPs) to finance full-time training or education for themselves or their partner.
Please review Filing taxes in Canada on the student services website for more information.
Applicants have access to the cost estimator to develop a financial plan that takes into account various income sources and expenses.
108 students graduated between 2005 and 2013: 2 graduates are seeking employment; for 11 we have no data (based on research conducted between Feb-May 2016). For the remaining 95 graduates:
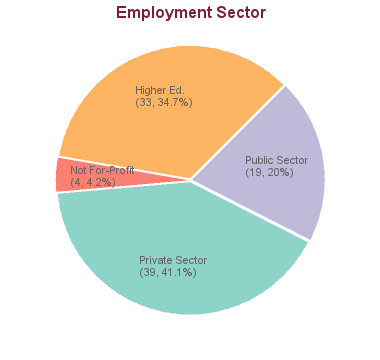
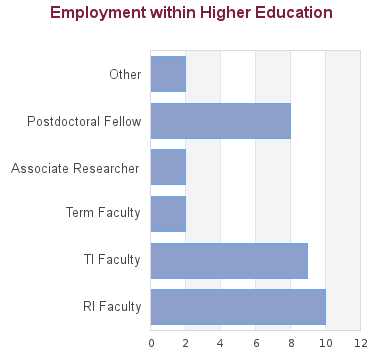
These statistics show data for the Doctor of Philosophy in Physics (PhD). Data are separated for each degree program combination. You may view data for other degree options in the respective program profile.
| 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Applications | 102 | 90 | 103 | 94 | 86 |
| Offers | 25 | 16 | 19 | 13 | 19 |
| New Registrations | 14 | 14 | 14 | 10 | 16 |
| Total Enrolment | 111 | 114 | 112 | 111 | 116 |
Students in research-based programs usually require a faculty member to function as their thesis supervisor. Please follow the instructions provided by each program whether applicants should contact faculty members.
These videos contain some general advice from faculty across UBC on finding and reaching out to a supervisor. They are not program specific.
This list shows faculty members with full supervisory privileges who are affiliated with this program. It is not a comprehensive list of all potential supervisors as faculty from other programs or faculty members without full supervisory privileges can request approvals to supervise graduate students in this program.
| Year | Citation |
|---|---|
| 2023 | Quite surprisingly, some quantum systems can encode gravitational physics in a higher dimensional space. Dr. Waddell used this fact to study a key quantum system arising in string theory, to show that information about a black hole's contents is not destroyed when it evaporates, and to propose a quantum description of universes similar to our own. |
| 2023 | Dr. Haenel studied the signatures of the Higgs mode in exotic superconducting materials. The Higgs mode emerges as a quasiparticle in the framework of superconductors. It is the condensed-matter-analogue of the Higgs Boson in the the Standard Model. Research on these collective excitations in superconductors can lead to a better understanding of the mechanism of high temperature superconductors. |
| 2023 | Dr. Ripoche studied evolved stellar populations, from giant stars to their remnants. He developed new tools to analyze data from X-ray space telescopes, measure distances in space, and identify dead stars, called white dwarfs, in large surveys. His findings will help us better understand the structure and history of our Galaxy and the Universe. |
| 2023 | Dr. Wang devised and carried out landmark experiments using radio-frequency and millimeter-wave fields to control and probe the evolution of ultracold molecular plasmas. His findings have provided new insights into ultracold neutral plasmas specifically, and into disordered many-body systems in general. |
| 2023 | Where do the chemical elements come from? Using the nuclear physics technique of mass spectrometry, Dr. Jacobs investigated potential astrophysical sites where some of these elements are produced. The findings point to binary neutron star mergers as a prime candidate for explaining a range of elemental abundances observed in stars. |
| 2023 | Dr. Pinsonneault-Marotte participated in the realisation of the Canadian Hydrogen Intensity Mapping Experiment telescope and analysis, which resulted in a preliminary detection of hydrogen located nearly 11 billion light-years away. |
| 2023 | Dr. Fomichev developed computational methods for predicting the properties of materials with strong electron-lattice interactions. Applying these methods to organic solar cell materials, he showed that lattice vibrations can break apart excitons to generate electricity, potentially explaining how this novel technology operates on an atomic scale. |
| 2023 | Dr. Reynolds used experiments in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance to correct assumptions made in clinical practice about how fats and water interact in the human brain during an MRI scan, affecting accurate measurements. In doing so, he further developed a model of nuclear relaxation leading to a potential new form of contrast in MRI images. |
| 2023 | Dr. Bevington developed image processing and analysis algorithms for human brain imaging data. These algorithms help provide more accurate and precise images of the healthy and diseased brain. They are being applied in clinical research studies that are discovering alterations to dopamine release and brain energy production in Parkinson's disease. |
| 2023 | Dr. Dvorak developed a method for performing magnetic resonance imaging about 25 times faster than conventional techniques, while simultaneously improving the image quality. This method is implemented for scanners from 3 different manufacturers, including a small, portable, inexpensive scanner that could revolutionize access to MRI medical imaging. |
Physics provides research opportunities in many subfields of physics, including
Departments/Programs may update graduate degree program details through the Faculty & Staff portal. To update contact details for application inquiries, please use this form.

Here, you can choose from more than 300 graduate degree program options and 2000+ research supervisors. You can even design your own program.